A Book vs. B Book Brokers: Understanding the Key Differences
Share this publication:
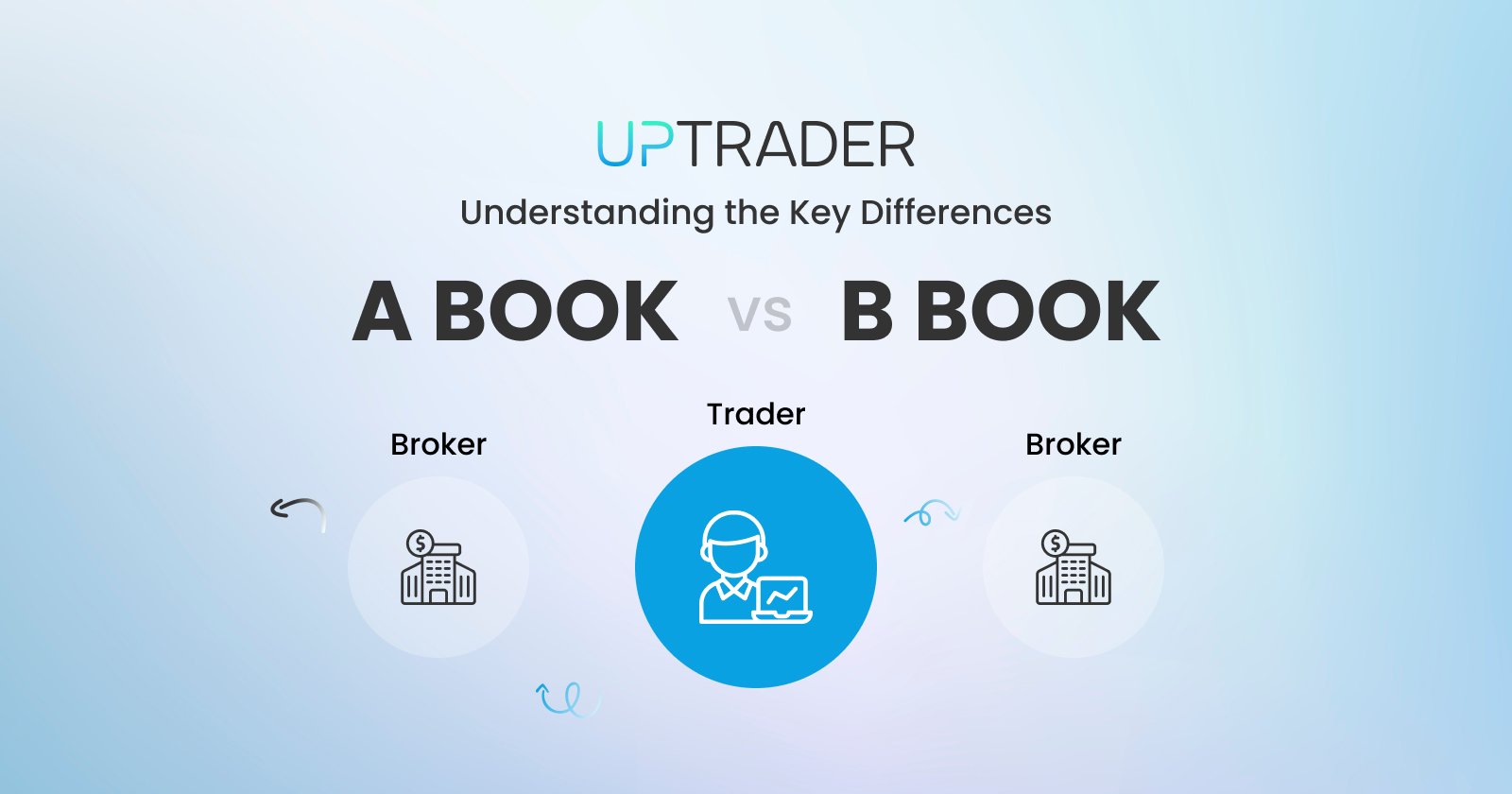
Brokers, being intermediaries between the market and traders, are one the key elements in the world of forex and CFD trading. There are two main ways in which the brokers close the client's trades, these include A Book and B Book. These words explain the order flow within brokers, the process of order filling, and risk management. It is important for every trader intending to pick a suitable broker to understand why there is a need to choose between the two models. Hence, in this article, we will examine A Book vs B Book brokers, and find out what they are, differentiate them, and their benefits.
What is an A Book Broker?
An A Book broker is also referred to as a Straight Through Processing (STP) or No Dealing Desk (NDD) broker and is a kind of brokerage that takes client orders and sends them directly to the market or other liquidity sources. This particular model ensures that the broker never takes the other side of the customers’ trade but instead passes the order on to an interbank market or a liquidity provider that will execute the trade. To put it differently, in this scenario the trader communicates via a broker and the broker seeks his payment in a broader market.
How A Book Brokers Operate:
- Execution Model: In an A Book setup, the orders made by the client are first sent through the broker and then to several other agents in the trading network which are usually banks and financial institutions where the orders are completed at the market price prevailing at that time.
- Profit Structure: A Book brokers typically make money by charging a commission per trade or through spreads (the difference between the bid and ask price). Because they do not take the opposite side of the trade, there is no inherent conflict of interest between the broker and the trader.
- Transparency: These brokers are often commended for their fair practices because the trade is carried out according to the real available market conditions and the rates are straight from the outside market.
Advantages of A Book Brokers:
- No Conflict of Interest: When it comes to trading, there are no grounds for the clients of A Book brokers to lose their money, as the orders are transacted on the market. Such a cautious approach creates confidence in the minds of the traders who do not wish to be subjected to unfair trading practices.
- Market Execution: Traders enjoy low pricing and quick execution speeds, which are key for scalpers and traders in a volatile period.
- Regulated Environment: The majority of A Book brokers are licensed and comply with certain policies, which prevent clients’ money and trades from being misused.
What is a B Book Broker?
On the contrary, a B Book brokerage employs a different approach and incorporates the client trades within its own books. This means that orders are not sent to an external market, so why does a B Book broker keep hold of these trades there? When a trader puts in an order the broker fills it as the opposite party. In this situation, if the trader wins, the broker loses and conversely, if the trader loses, the broker wins.
How B Book Brokers Operate:
- Execution Model: The B Book approach revolves around managing all client trading activities “in-house.” The broker takes the opposite position of the client, figuring out the odds that the majority of the traders will lose in the long run.
- Profit Structure: B Book brokers earn profits primarily from client losses. Unlike A Book brokers, these brokers may not charge commissions on trades, attracting new clients with the appeal of commission-free trading.
- Risk Management: For effective operations, successful B Book brokers need advanced risk management tools to control the win and loss of clients. For example, some may limit the risk exposure on large or aggressive positions via the external market by sending part of the trades.
Advantages of B Book Brokers:
- Lower Costs: B Book brokers often offer tighter spreads and zero-commission trading, making them appealing to beginners and traders looking to minimize expenses.
- Flexible Account Offerings: They may offer attractive promotions, bonuses, and educational resources to encourage more trading activity.
- Simplified Trading: With trades executed in-house, clients may experience less slippage and faster execution during normal market conditions.
A Book vs. B Book: Key Differences
Now that we’ve defined what A Book and B Book brokers are, let’s explore the fundamental differences between them - A Book vs B Book by main features:
- Order Execution:
- A Book: Orders are forwarded to an external liquidity provider hence they are executed at the market price. More often than not, traders enjoy better prices which are designed to reflect the market prices accurately. e. no slippage.
- B Book: On the other hand, orders are retained in the system of the brokers. With this internal execution, the broker can become the counterparty and as such, may manage the executions to improvements advantageous to them.
- Profit Model:
- A Book: Revenue streams consist of the charges made or the increases applied on the spread. The broker’s main focus therefore is to ensure that the clients are executed the best possible trades without slippage or delays.
- B Book: Clients’ losses are on the other hand the main source of income. The brokerage’s welfare is dependent on the poor performance of the traders and hence, creates a dilemma.
- Transparency and Trust:
- A Book: These models are preferred as all trades are done on live markets with actual market prices and the broker performs only brokerage functions. Such transparency is usually welcomed by seasoned and professional traders.
- B Book: Fair trade practices are often questioned with most of the B Book brokers as there is usually an in-built conflict of interest, coupled with the fact that many of these brokers are unregulated and carry out their business in a black box manner.
- Regulation and Oversight:
- A Book: Due to their structure, a good number of A Book brokers are obeying the laws and even seeking to be regulated by such financial authorities as the FCA, CySEC, and ASIC. This is an encouraging factor to be considered by the traders.
- B Book: Some B Book brokers are certified and properly conduct themselves, however the system itself may invite dishonest players. Checking a broker's regulatory status is vital for any trader.
- Client Experience:
- A Book: Typically offers market-oriented experiences, suitable for traders who value transparent pricing and are willing to pay for it through spreads or commissions.
- B Book: May provide a more tailored or lower-cost trading experience, which can be attractive to less-experienced traders or those looking to avoid direct trading fees. However, the client experience may vary significantly depending on the broker’s practices.
How to Choose Between A Book and B Book Brokers
Choosing between an A Book and a B Book broker depends on your trading style, experience, and priorities. Here are some key factors to consider:
Trading Strategy: If your trading strategy requires some form of high-speed trading or scalping strategies, it is advisable to go with an A Book broker since they have direct market access and sufficient speed for execution. In contrast, if you sometimes trade but appreciate low spreads and no fees, you may consider trading with a B Book broker since it will be cheaper to trade.
Trust and Regulation: Make sure that you always check the regulatory status of a broker. A Book brokers tend to be more regulated because they tend to provide more honest services, however, that doesn’t mean that B Book brokers are all crooked. By looking for brokers who are regulated by such authorities and have positive reviews from the clients over the years.
Cost Structure: Compare the costs, spreads, commissions, and the two business models. More often than not A Book brokers will charge a certain commission and B Book brokers might compensate for the absence of a commission by widening the spreads or hidden costs.
Risk Appetite: If you are uncomfortable with the idea of trading with a broker who will benefit from your losses, consider trading with an A Book broker for your convenience. On the other hand, if you believe in your trading strategy and do not mind higher trading costs, a trustworthy B Book broker may be suitable for you.
Conclusion and Final Thoughts
It is important to realize the differences between B Book and A Book brokers when it comes to choosing a brokerage. A Book brokers are the ones who execute client orders upon receipt and send them to the market in return for commissions or spreads. Such a model is transparent and encourages the broker to work by the principles of the client's success.
On the contrary, B Book brokers have no intention of sending traders’ orders to the market and instead profit from the losses of their clients presenting the services as commission-free which may create interest.
Both models have their own merits and demerits, and the ultimate decision lies with the trader in regard to his or her aspirations, experience, and tastes. Traders can take advantage of A Book vs. B Book understanding and tackle the brokerage puzzle easily where a trader takes on a partner that fits the trading demands and anticipations
If you want to make use of robust CRM solutions that can help your brokerage with affiliate programs, copy trading, and other many amazing features then talk to a consultant on our site today and request a demo!